Test your knowledge of global systems and migration with this 15-question A level quiz.
If you haven't already done it, work through the global systems and migration web enquiry on the PowerPoint - knowledge of the graphs in particular will be crucial for taking the quiz. Or look at it again to help fill any gaps in what you know!
HIGH SCORES
| Rank | Name | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | MAR | 31 |
| 2nd | sjv | 31 |
| 3rd | K.B | 31 |
| 4th | LUD | 31 |
| 5th | RBW | 31 |
| 6th | I.J | 31 |
| 7th | CEB | 31 |
| 8th | JOE | 31 |
| 9th | JLD | 31 |
| 10th | COW | 31 |
QUIZZES // Global systems and migration
Q1. Which of the following are push factors that cause migration?
Low incomes, few economic opportunities, poor housing and inadequate health care
Inadequate health care, low incomes, few economic opportunities and good housing
Poor housing, inadequate health care, low incomes and many economic opportunities
Few economic opportunities, poor housing, inadequate health care and high incomes
Q2. Which of the following are pull factors that cause migration?
Higher incomes, more economic opportunities, worse housing and healthcare
Fewer economic opportunities, better housing, better healthcare and higher incomes
Higher incomes, more economic opportunities, better housing and better healthcare
Better housing, better healthcare, lower incomes and more economic opportunities

Q3. Look at the map of the Human Development Index (HDI) on page 8 of the PowerPoint. Amongst other countries, HDI levels are highest in:
Australia, Chile, Russia, Mexico and Canada
Chile, Mongolia, Turkey, Canada and Australia
Russia, Turkey, Canada, Australia, China
Canada, Australia, Chile, Russia and Turkey

Q4. The flow diagram on page 9, outlining the relationship between migration and development, shows:
Investments directly result in economic growth and employment creation
Education directly influences economic growth and employment creation
Outmigration directly results in economic growth and employment creation
Well-being directly influences economic growth and employment creation
Q5. What are two benefits of emigration (two answers are correct)?
Remittances are sent to the destination country
Remittances are a form of economic leakage from the destination country
Remittances are sent to the source country
Remittance payments to family are spent in the local economy

Q6. Look at the financial inflows graph on page 13. What happened to foreign direct investment from 1990 to 2009?
Increased slowly until 2004, then increased at a faster rate
Increased constantly, reaching US$500bn in 2009
Increased slowly until 2001, then increased at a faster rate
Increased constantly, reaching US$600bn in 2009
Q7. How many rural migrant workers live in urban China?
231 million
251 million
271 million
291 million
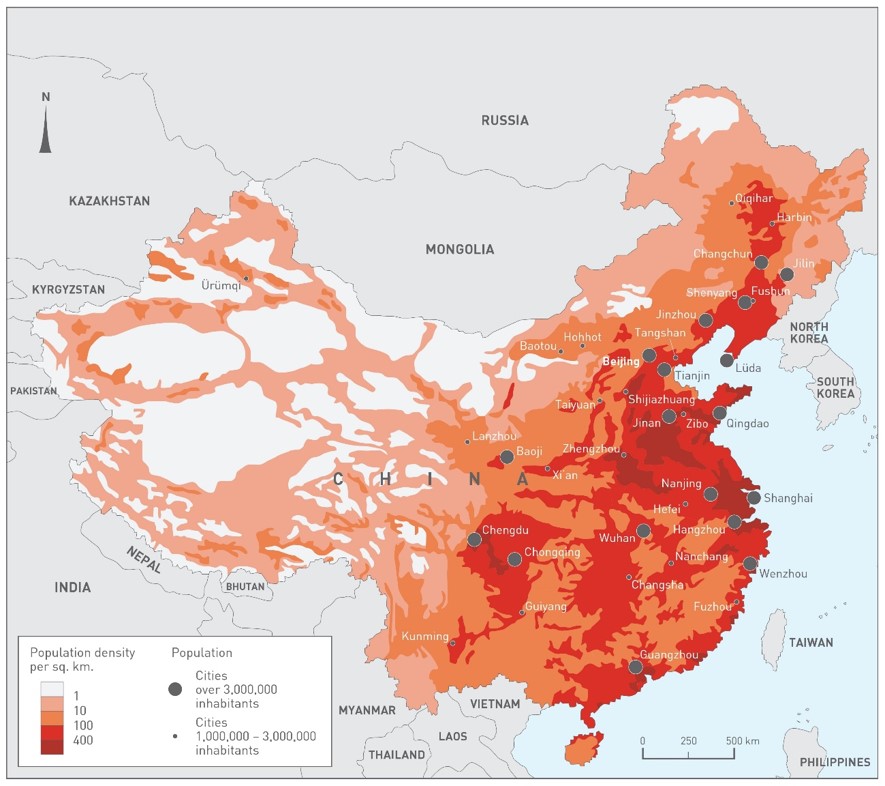
Q8. Look at the population density map of China on page 15. Which of the following Chinese cities are located in the most densely populated areas?
Jinan, Chengdu, Lanzhou and Guangzhou
Guangzhou, Jilin, Chengdu and Hangzhou
Chengdu, Hangzhou, Guangzhou and Jinan
Hohhot, Guangzhou, Jinan and Chengdu
Q9. Where do the most significant regional migration flows from Asia go (as shown by the graph on page 16)?
Asia, Europe and South America
Africa, North America and Asia
South America, North America and Europe
Asia, North America and Europe
Q10. What is a transit country?
Destination for migrants
Source country from which migrants leave
Country migrants travel through
Country which migrants avoid traveling through
Q11. Refugees are migrants who are forced to move. Why are they persecuted?
Race, religion, nationality or political opinion
Education, religion, nationality or political opinion
Race, sexuality, nationality or political opinion
Race, religion, gender or political opinion
Q12. What does the abbreviation IOM mean?
International Operations for Migrants
International Operations for Migration
International Organisation for Migration
International Organisation for Migrants
Q13. What does the Chinese household registration system (hukou) provide?
Government welfare
Access to resources
Internal migration control
All of the above
Q14. What is the definition of ‘diaspora’?
Migrants from a range of places
Migrants who have returned to their country of origin
Migrants from a specific place who have dispersed globally
Migrants who have lost touch with their country of origin
Q15. Where might migrants travelling from Africa to Northern Europe settle?
Spain, France, Italy or Greece
Italy, Georgia, Spain or France
France, Oman, Greece or Spain
Greece, Spain, Jordan or Italy
Finished!
You scored this time. The more correct answers you give, and the fewer incorrect answers you guess, the better your score.

